As an improved version of Oriented Strand Board (OSB), Fine Surface Oriented Strand Board (FOSB) features additional smooth layers compared to standard OSB. This enhancement gives it a smooth, refined finish that is ready for direct veneering. With mechanical properties rivaling solid wood, excellent solution, and a more affordable price, FOSB has become highly popular in the home furnishing market and is widely favored by furniture manufacturers.

Recently, some followers have asked google about the manufacturing process of Dekek's new environmentally friendly FOSB. We’ve taken this opportunity to put together a detailed introduction on how it is produced.
Dekek's new FOSB manufacturing is divided into the following stages based on the production workflow: raw material selection, flake preparation, drying, screening, blending, forming, hot pressing, and finishing.
1. Material Selection
Premium Eucalyptus & Consistent Quality
Dekek's new FOSB primarily uses fast-growing eucalyptus wood with a tree age of 3–5 years as the raw material. Eucalyptus is recognized in China’s panel industry as a high-quality raw material due to its uniform wood species, knot-free characteristics, hard texture, strong nail-holding capacity, consistent quality, and pure, even color.

(Located in Guangxi: Premium Fast-Growing Eucalyptus Forests)
Guangxi boasts exceptionally rich forest resources, which is one of the key reasons Dekek chose to establish its production base here. In 2021, the forest stock in Guangxi reached approximately 978 million m³, with an annual timber output of about 39 million m³. The area of planted forests (including pine, fir, and eucalyptus) spans 134 million mu, accounting for about one-tenth of the national total and ranking first in China. (Source: Guangxi Forestry Department)
Dekek has established deep strategic partnerships with several leading forest farms, including Dongmen Forest Farm, Qipo Forest Farm, Quli Overseas Chinese Forest Farm, Xichang Overseas Chinese Forest Farm, and Guangxi Forest Farm. With an annual logging capacity of up to about 1.1 million m³, Dongmen Forest Farm also hosts Asia's largest eucalyptus gene bank and ranks among the top providers of high-quality tree varieties in the country.
2. Flake Production Stage
Ensuring Flake Purity & Controllable Quality
2.1 Flake Production Using a Longwood Flaker
Eucalyptus logs are first fed via a conveyor into a drum debarker. Since bark often contains impurities such as sand, small stones, and metals, the debarker thoroughly removes the bark to ensure the produced flakes are clean and neat. This results in final panels free from impurities or bark spots.
The debarked logs are then fed in batches into the cutting chamber of a longwood flaker, where they are sliced into flakes. The processed flakes are transported by conveyor to a wet flake storage bin, while the bark and wood residues are discharged and used as fuel for the energy center.
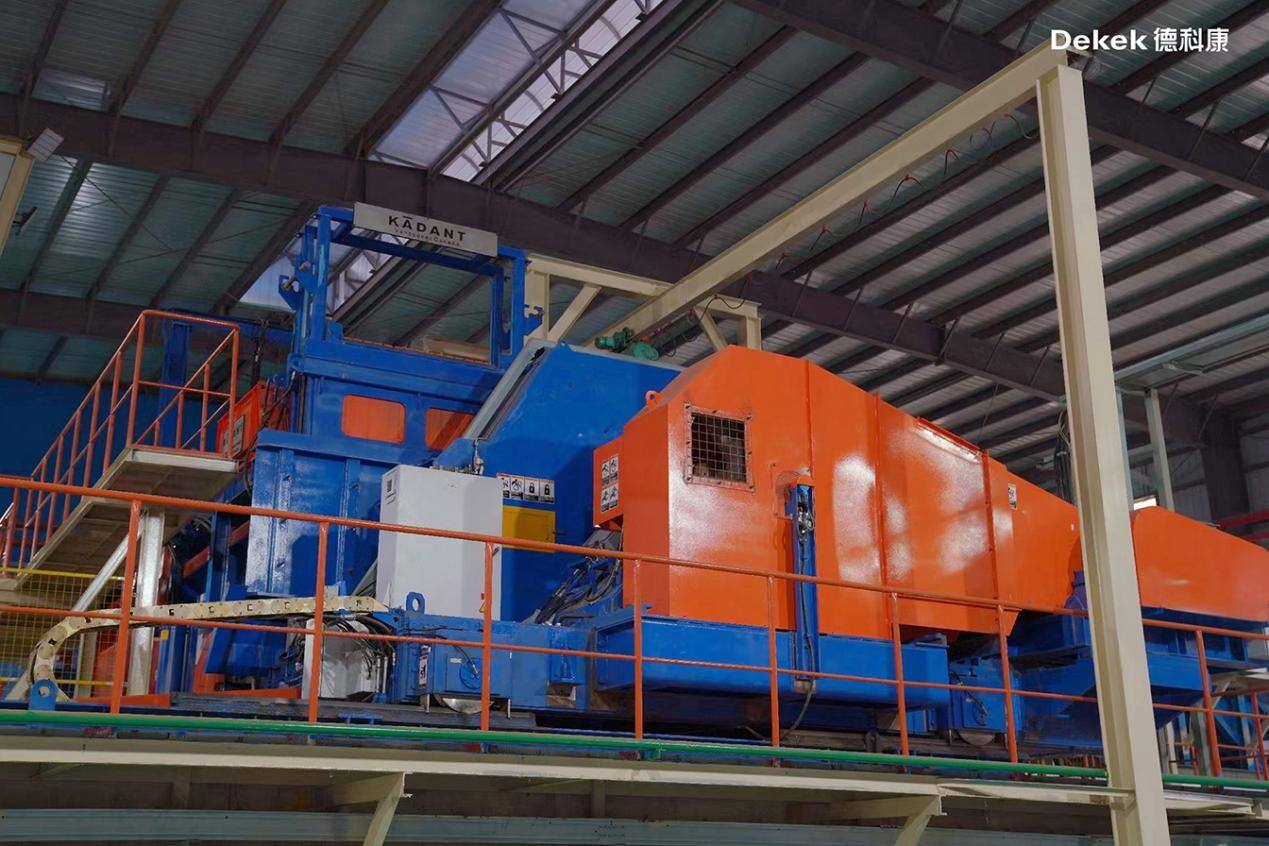

(Kadant Longwood Flaker – Canada)
2.2 Two-Stage Process for Fine Flake Production
The two-stage processing technology enables the use of lower-grade wood materials such as twigs, crooked timber, and sawmill scraps to produce qualified flakes. This approach helps alleviate raw material shortages to some extent.
The smaller wood materials, including branches, are first fed into a drum chipper for chipping. After passing through a metal detector, the chips are conveyed to a ring flaker for further refining. The fine flakes produced by the ring flaker, along with the larger flakes from the longwood flaker, are then transported via conveyor to a horizontal metering bin for storage.
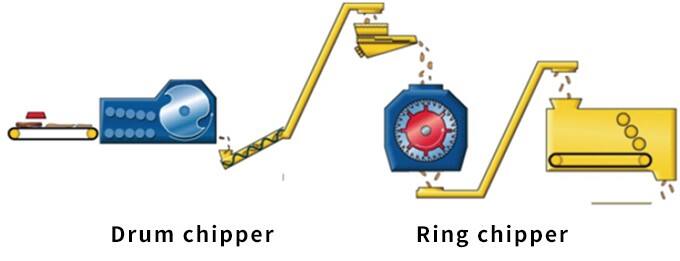
(Schematic Diagram of the Two-Stage Preparation Process)
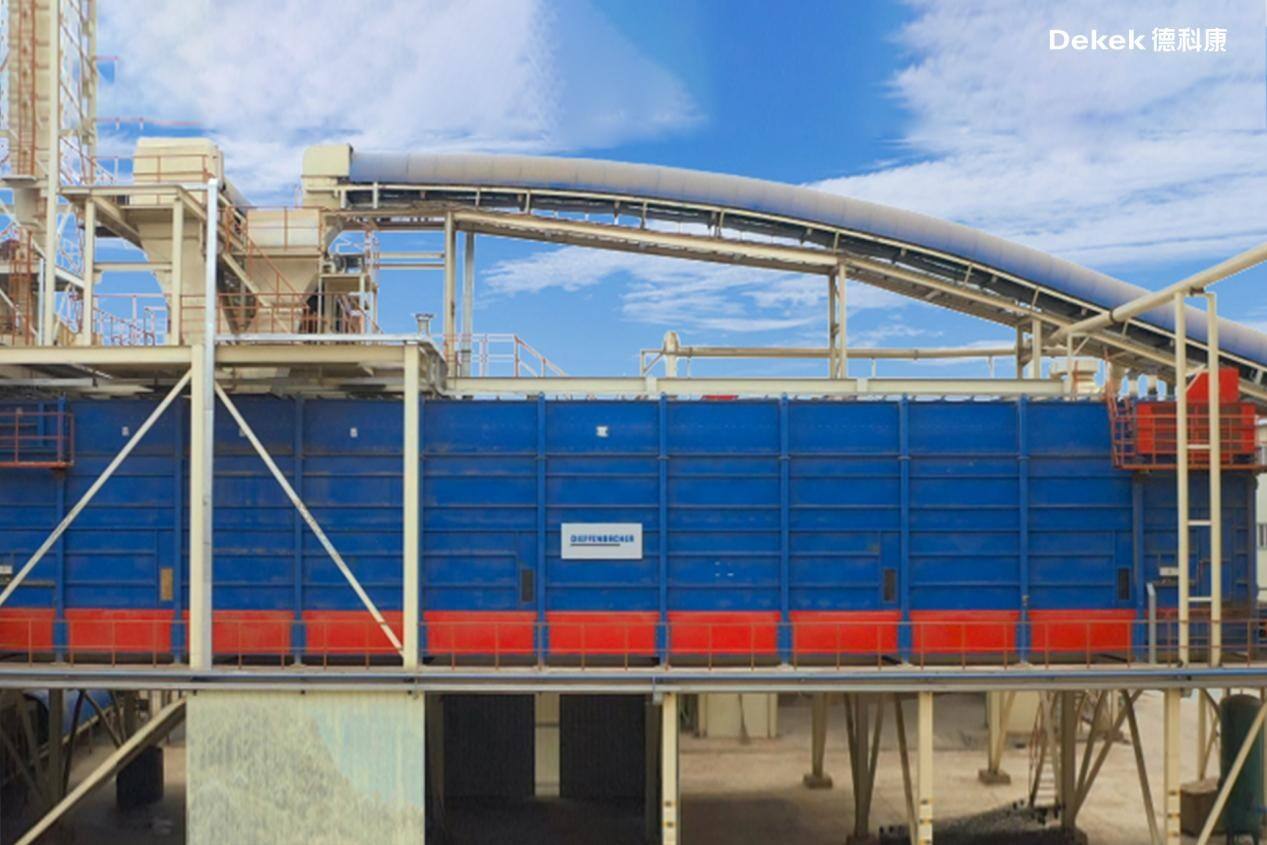

(German Dieffenbacher long horizontal measuring double material warehouse)
3. Drying Stage
Segmented Drying & Uniform Moisture Content of Flakes
Wet flakes are continuously and evenly fed by a discharge device into a 32-meter-long rotary dryer for drying. The thermal energy required is supplied by high-temperature flue gas from the energy center. The entire drying process is divided into three stages: pre-drying, main drying, and conditioning, which directly dry the flakes through thermal convection and conduction.
Due to their small size and light weight, fine flakes pass through the dryer rapidly. In contrast, larger flakes tumble along the inner wall of the dryer, remaining inside for a longer period and traveling a greater distance compared to the finer particles.
Despite varying initial moisture levels, all types of flakes achieve uniform moisture content after processing in the same rotary dryer, with the final moisture content controlled within the range of 4–6%.
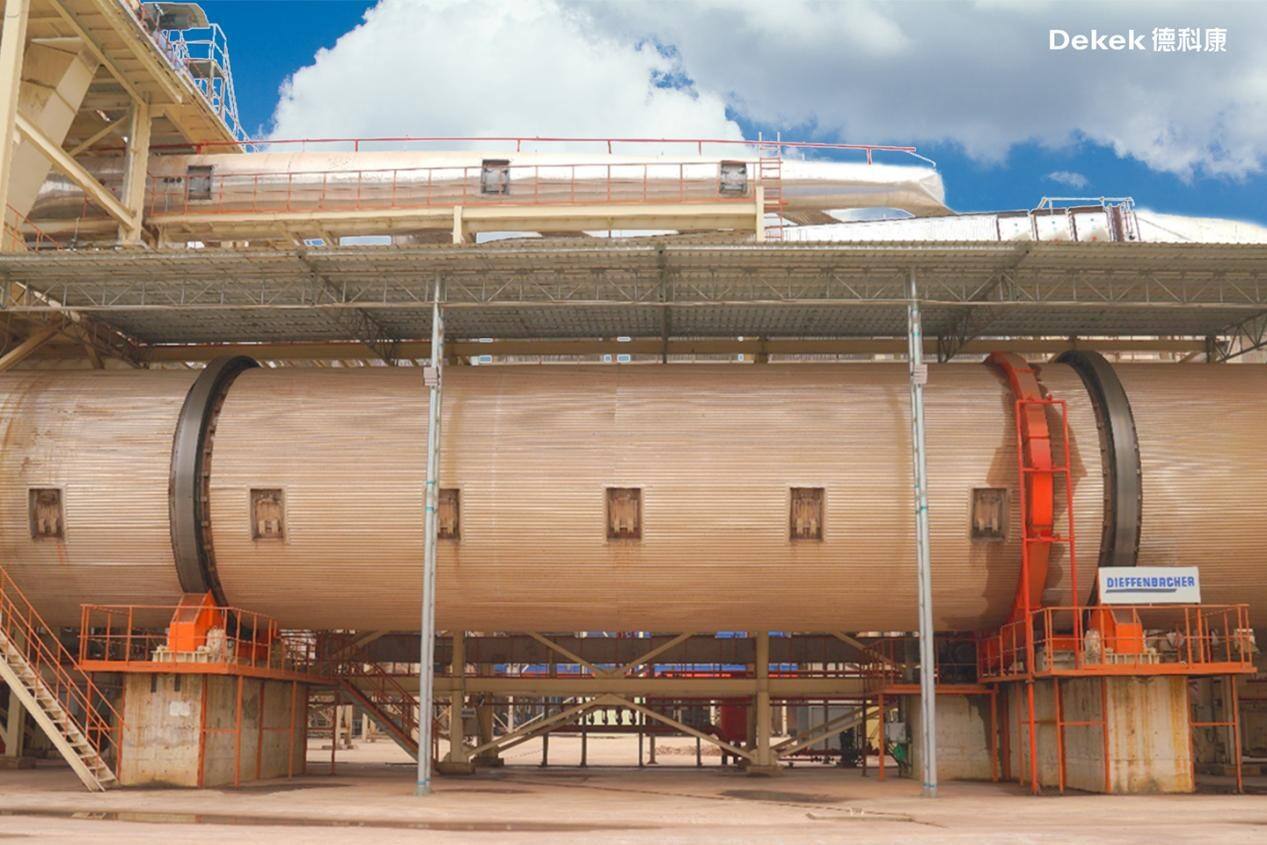
(DIEFFENBACHER Rotary Dryer – Germany)
4. Screening Stage
Controlling Core Layer Ratio & Ensuring Fine Surface Material Quality
The dried flakes are transported via piping to a super sorter for size-based classification, while extremely fine impurities such as sand and dust are simultaneously removed. The sorted fine flakes are then refined by three screening mills into fine surface material, which is stored in a dedicated surface material silo.

(CMC Super Sorter – Italy)

(Screening Mill)
5. Blending Stage
Preserving Flake Integrity & Ensuring Uniform Glue Application
The surface and core layer flakes are accurately metered and separately fed into rotary blenders. A precisely proportioned amount of MDI adhesive is injected into each blender. As the drum rotates, the flakes are repeatedly lifted and dropped, ensuring thorough and even coating. The retention time of the flakes inside the blender can be adjusted according to process requirements.
This blending method offers significant advantages: the absence of internal mechanical forces preserves the physical structure of the flakes. The repeated free-fall tumbling action within a controlled cycle ensures consistent and uniform adhesive application.

(MDI Adhesive Storage Tank)
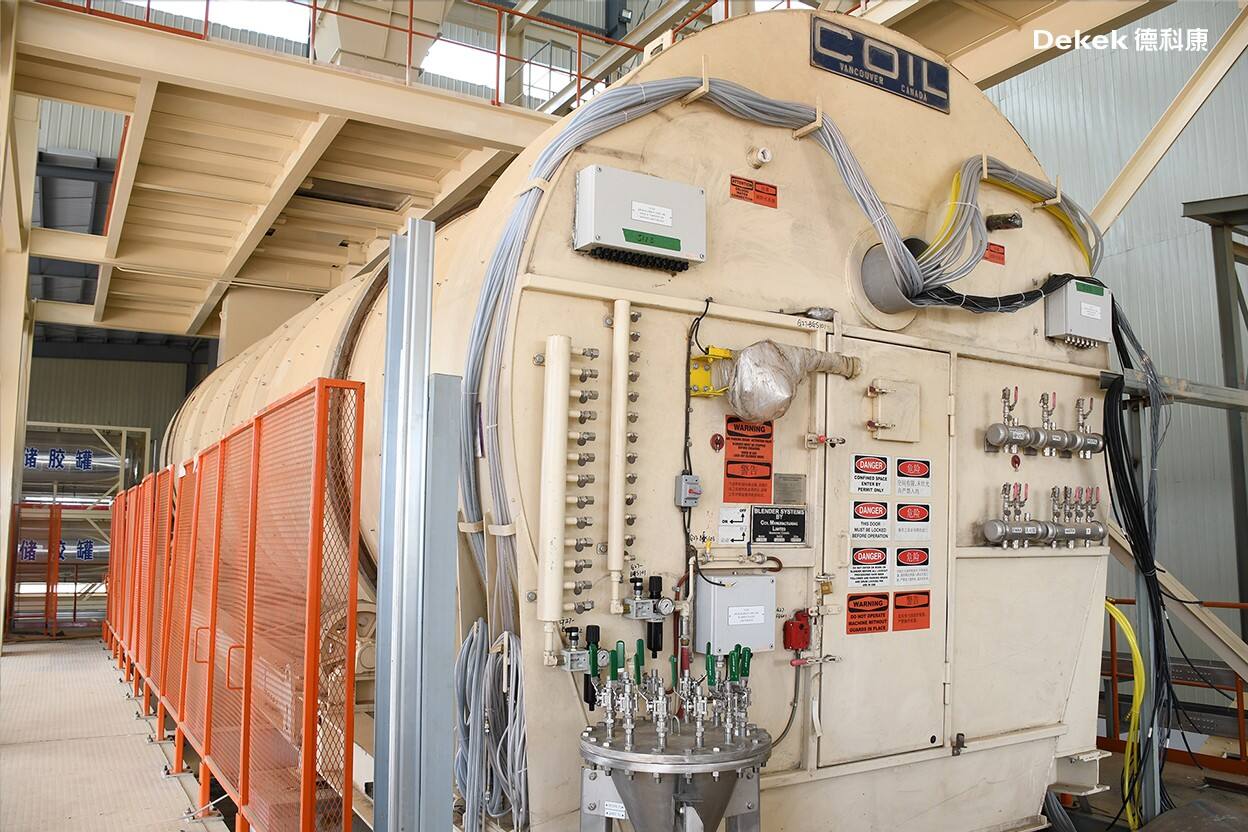

(DIEFFENBACHER Blending System – Germany)
6. Forming Stage
Ensuring Orientation Accuracy & Minimizing Density Deviation
The glued surface and core layer flakes are conveyed separately to their respective metering bins. These bins automatically and evenly control the discharge of the flakes, which are then precisely distributed through four forming heads.
The forming equipment utilizes an air-flow principle to create a fine surface structure on the top and bottom layers. The two middle layers feature horizontally oriented flakes, while the core layer consists of longitudinally aligned flakes. This cross-directional arrangement gives Dekek's new FOSB exceptional dimensional stability and modulus of rupture (MOR), with strong nail-holding capacity on both the surface and edges.
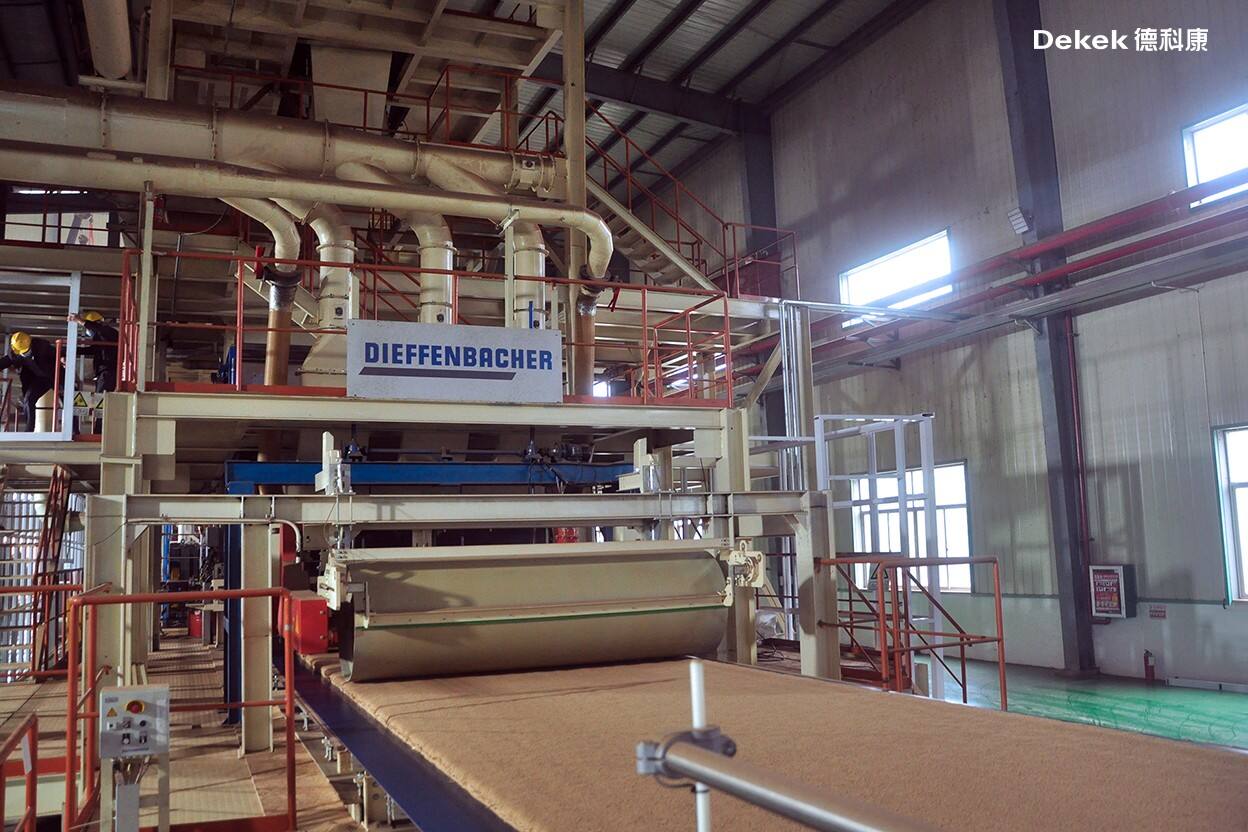

(DIEFFENBACHER Five-Layer Oriented Forming System – Germany)
7. Hot Pressing Stage
Continuous Hot Press Forming & Uniform Density and Thickness
The formed mat enters a pre-press for initial compaction. After passing through a metal detection stage, the pre-pressed mat is fed into a 40-meter-long continuous press. Here, it undergoes continuous hot pressing under simultaneous high temperature and pressure to achieve final formation.
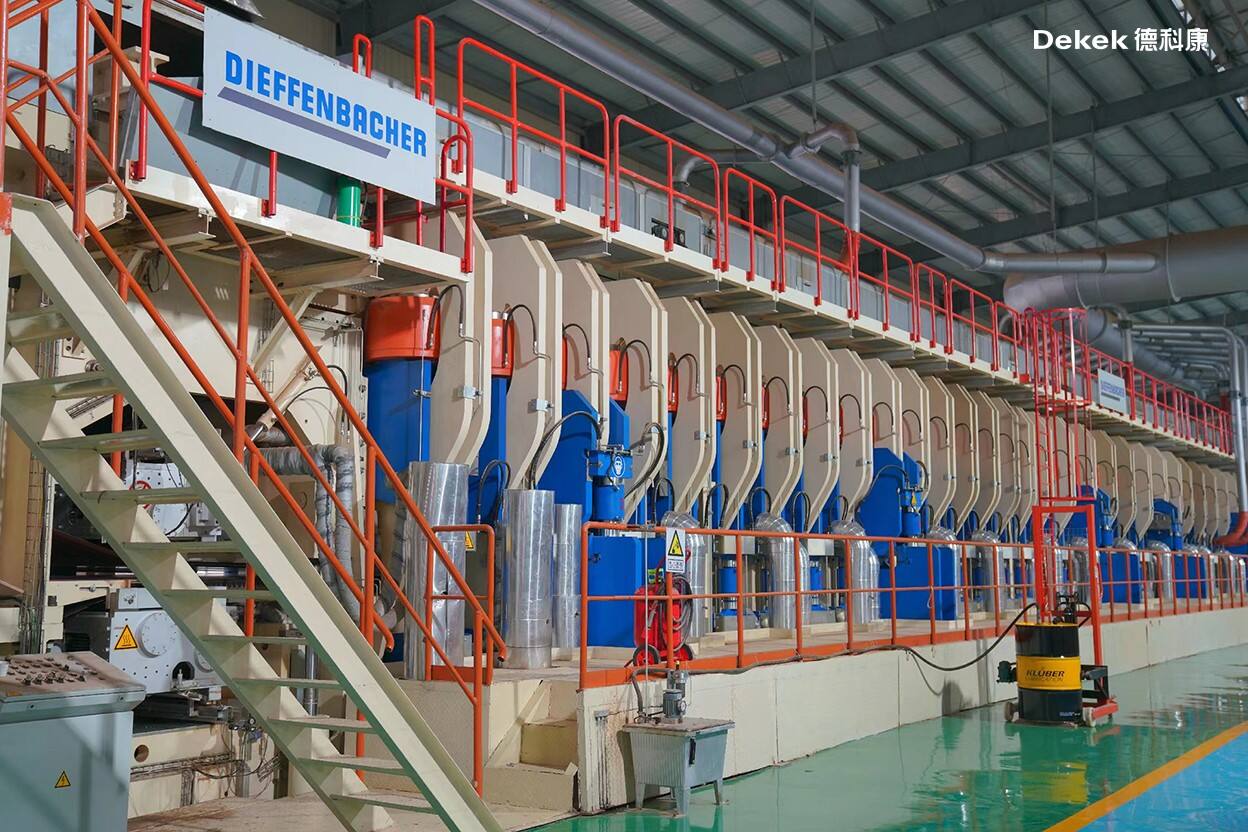

(DIEFFENBACHER Continuous Hot Press System – Germany)
8. Finishing Stage
Automated Control & Customized Processing
The freshly pressed board undergoes edge trimming and cross-cutting before entering a cooling and turnover system. After cooling, the boards are stacked and transferred to an intermediate storage system for a 72-hour conditioning period.
Following storage, the boards are first processed through a sander for three stages: rough, fine, and precision sanding. They are then cut to specified dimensions in the cutting center to produce finished panels. The final boards are graded based on quality, inspected, and stacked. An automated laser etcher marks identification codes on the edge of each board before packaging. The finished products are then stored in the warehouse awaiting shipment.
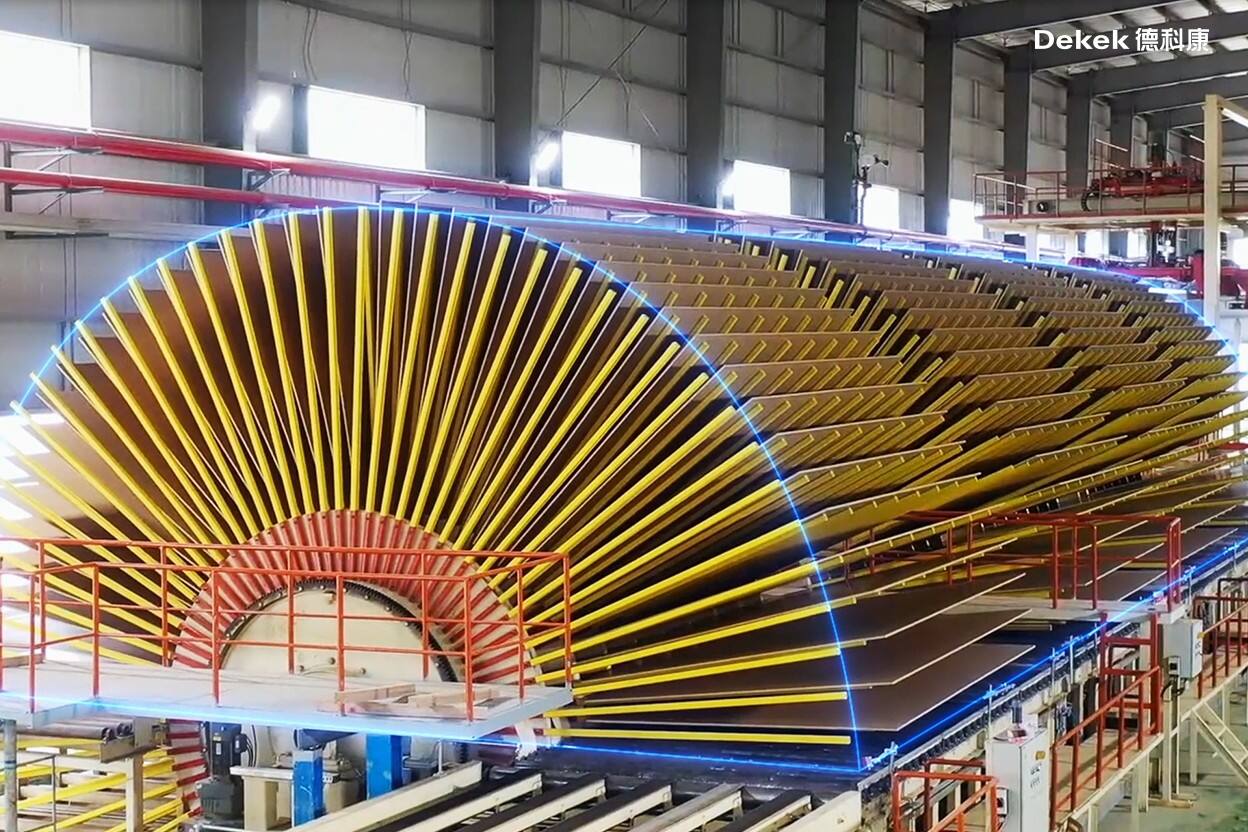

(Board Turner Cooling)
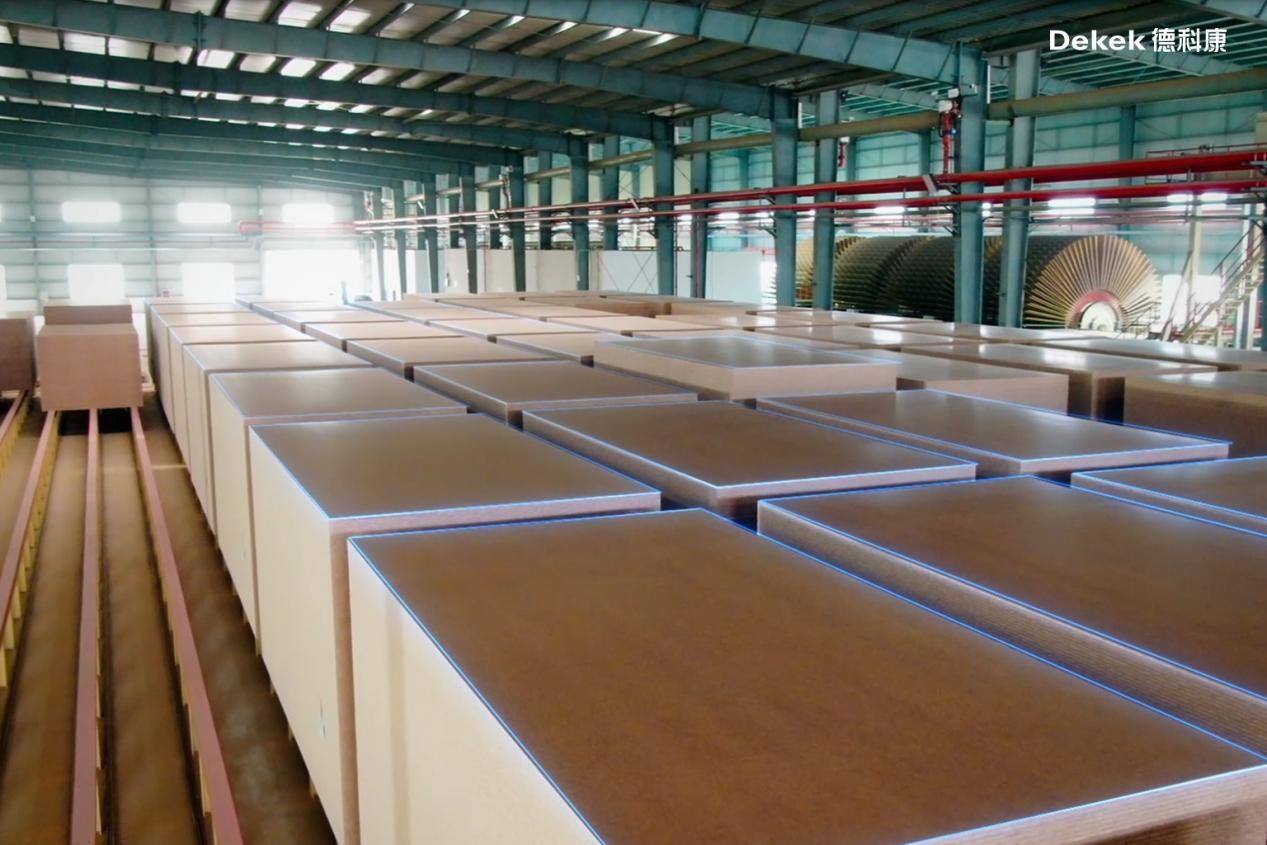

(Conditioning in Intermediate Storage System)
This concludes the production process of Dekek's new FOSB. As a perfect integration of eucalyptus raw materials and advanced equipment, Dekek FOSB exhibits exceptional internal bond strength, modulus of rupture (MOR), and resistance to creep. These properties make it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, including building materials, interior decoration, furniture manufacturing, flooring substrates, door cores, packaging, and structural panels. It stands as a premium, health-conscious, and environmentally friendly new-generation material.